Ventricular Fibrillation Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia: Difference between revisions
From Protocopedia
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
*Consider sedation in patient experiencing cardioversion or defibrillation by their own AICD. | *Consider sedation in patient experiencing cardioversion or defibrillation by their own AICD. | ||
* Leave copy of ECG at ER on any patient with implanted device. | * Leave copy of ECG at ER on any patient with implanted device. | ||
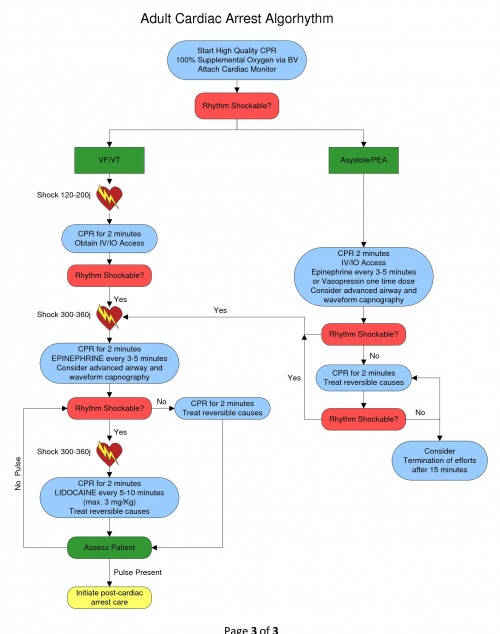
[[File:Adult_Cardiac_Arrest_Flowchart.jpg|500px]] | |||
Revision as of 17:46, 3 May 2012
Section 4 - CARDIAC
4.08 CARDIAC ARREST - VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION /PULSELESS VENTRICULAR TACHYCARDIA
Ventricular Fibrillation (VF) and Pulseless V-Tach (VT) focuses in the correction of the dysrhythmia into a pulse producing rhythm. Consider all possible reversible causes for cardiac arrest utilizing a national recommended mnemonic of “H’s and T’s”:
| H’s | T’s |
|---|---|
| Hypovolemia | Tension Pneumothorax |
| Hypoxia | Tamponade, cardiac |
| Hydrogen Ion (acidosis) | Toxins or Tablets (overdose) |
| Hypo/hyperkalemia | Thrombosis, pulmonary |
| Hypothermia | Thrombosis, cardiac |
In addition, also consider the following:
| Hypoglycemia | Trauma |
When the Patient found in cardiac arrest:
- Initiate BLS algorhythm with 5 cycles of high quality CPR (push hard/push fast)
- Minimum of 100 compressions per minute, minimize interruptions
- Compression rate of 30:2 for approximately 2 minutes
- Depth of compression of at least 2 inches
- Initiate the use of a mechanical compression device if available
- Assist ventilations with OXYGEN @ 100% via BVM - DO NOT HYPERVENTILATE
- Attach cardiac monitor – Evaluate the cardiac rhythm
- VF/VT Present – deliver a DEFIBRILLATION 120-200j biphasic
- Continue high quality CPR/Ventilations for 2 minutes
- Establish intravenous access via IV or IO
- Consider advanced airway procedure using supraglottic airway (king tube) or endotracheal intubation
- Do not interrupt compressions to place an advanced airway
- Confirm tube placement with capnography (a range 5-20 mmHg is indicative of low cardiac output)
- Administer EPINEPHRINE 1:10,000 1 mg IV / IO – repeat every 3-5 minutes of arrest
OR
- Administer VASOPRESSIN 40 units IV / IO – replaces the first or second dose of epinephrine
- Vasopressin is a one-time dose
- Do not stop CPR to administer medications
- Reassess for circulation every two minutes
- VF/VT Present – deliver a DEFIBRILLATION 300-360j biphasic
- Subsequent shocks should be at the higher dose selected
- Administer LIDOCAINE 1 to 1.5 mg/kg IVP. May repeat every 5-10 minutes to a maximum of 3 mg/Kg
- If VF/VT converts to a pulse-producing non-heart block supraventricular rhythm, administer a LIDOCAINE DRIP 1-4 mg/min
- In patients over age 70 or in those with known hepatic disease, reduce LIDOCAINE boluses at 0.25 mg/kg every 3 minutes to a maximum of 1.5 mg/kg
- Administer MAGNESIUM SULFATE 2 gm IVP only if suspected Polymorphic VT (Torsades de pointes) or hypomagnesemic state (chronic alcohol, diuretic use)
- Administer SODIUM BICARBONATE 1 mEq/kg IVP if suspected, HYPERKALEMIA (e.g. dialysis patient), or Tricyclic antidepressant OD
If patient combative post resuscitation, refer to ANALGESIA / SEDATION PARAMETER (2.04)
Deliver all Defibrillations at 360 Joules in any patient who has had an Automatic Implanted Cardioverter Defibrillator (AICD) shock. (Use Anterior/Posterior position if possible for Defibrillator Pads - Do not place pads over device).
- Consider sedation in patient experiencing cardioversion or defibrillation by their own AICD.
- Leave copy of ECG at ER on any patient with implanted device.